The container shipping route from China to the United States is one of the world's busiest and most crucial maritime trade lanes. Understanding the factors that influence shipping rates on this route is essential for businesses engaged in trans-Pacific trade. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of container shipping rates from China to the US, their determinants, historical trends, and future outlook.
1. Overview of China-US Container Shipping
The China-US shipping route is a cornerstone of global trade, facilitating the movement of a vast array of goods from the world's largest exporter to its largest consumer market. Key aspects of this trade lane include:
Major Chinese ports: Shanghai, Ningbo-Zhoushan, Shenzhen, Guangzhou
Primary US destination ports: Los Angeles, Long Beach, New York/New Jersey, Seattle/Tacoma
Typical transit times: 14-30 days, depending on specific routes and stops
Main types of cargo: Electronics, machinery, textiles, furniture, toys
2. Components of Container Shipping Rates
Container shipping rates from China to the US are composed of several elements:
2.1 Base Freight Rate
This is the fundamental charge for moving a container from the origin port in China to the destination port in the US. It's typically quoted per container (20ft or 40ft).
2.2 Bunker Adjustment Factor (BAF)
A surcharge that fluctuates with fuel prices, allowing carriers to pass on changes in fuel costs to shippers.
2.3 Terminal Handling Charges (THC)
Fees for loading and unloading containers at both origin and destination ports.
2.4 Peak Season Surcharge (PSS)
An additional fee applied during high-demand periods, typically from July to October.
2.5 Documentation and Administrative Fees
Charges for processing shipping documents and other administrative tasks.
2.6 Security Surcharges
Fees related to security measures and compliance with international security standards.
3. Factors Influencing China-US Container Shipping Rates
Numerous factors affect shipping rates on this crucial trade lane:
3.1 Supply and Demand Dynamics
The balance between available shipping capacity and cargo volumes significantly impacts rates. When demand outstrips supply, rates tend to rise, and vice versa.
3.2 Fuel Prices
As a major component of operating costs, fluctuations in fuel prices can lead to significant changes in shipping rates.
3.3 Geopolitical Factors
Trade tensions, tariffs, and international relations between China and the US can influence trade volumes and, consequently, shipping rates.
3.4 Seasonal Variations
Demand for shipping typically peaks in the months leading up to the holiday shopping season in the US, often resulting in higher rates.
3.5 Infrastructure and Capacity
Port congestion, availability of containers, and overall shipping capacity can affect rates.
3.6 Currency Exchange Rates
Fluctuations in the USD-CNY exchange rate can impact the relative cost of shipping.
3.7 Regulatory Changes
New environmental regulations or safety standards can lead to increased operational costs for carriers, potentially affecting rates.
4. Historical Trends in China-US Container Shipping Rates
Understanding historical rate trends provides context for current market conditions:
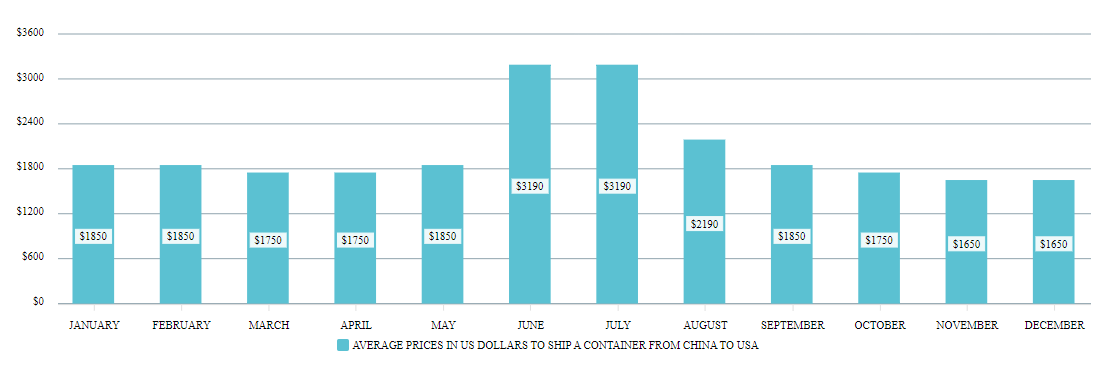
4.1 Pre-2020 Era
Before 2020, rates on the China-US route were relatively stable, with typical fluctuations driven by seasonal demand and fuel price changes. Average rates for a 40ft container ranged from $1,500 to $2,500.
4.2 2020-2021: Pandemic-Induced Volatility
The COVID-19 pandemic caused unprecedented disruptions:
Initial drop in rates due to reduced demand
Subsequent surge as consumer spending shifted to goods
Peak rates reached over $20,000 per 40ft container
Supply chain bottlenecks and port congestion exacerbated rate increases
4.3 Recent Stabilization
As of 2024, rates have largely stabilized but remain higher than pre-pandemic levels. Current average rates for a 40ft container range from $3,000 to $5,000, subject to market fluctuations.
5. Current Market Situation
The current state of China-US container shipping rates is characterized by:
Gradual normalization of supply chains post-pandemic
Ongoing capacity management by major shipping alliances
Increased focus on long-term contracts to mitigate rate volatility
Growing emphasis on digitalization and transparency in pricing
6. Rate Comparison Across Major Routes
To provide context, it's useful to compare China-US rates with other major global shipping routes:
| Route | Average Rate (40ft container) |
|---|---|
| China to US West Coast | $3,500 - $4,500 |
| China to US East Coast | $4,500 - $5,500 |
| China to Europe | $3,000 - $4,000 |
| Europe to US East Coast | $2,500 - $3,500 |
Note: These rates are indicative and can vary significantly based on current market conditions.
7. Strategies for Managing Shipping Costs
Businesses can employ several strategies to manage their shipping costs on the China-US route:
7.1 Contract Negotiations
Negotiating long-term contracts with carriers can provide rate stability and guaranteed capacity.
7.2 Timing of Shipments
When possible, avoiding peak shipping seasons can result in lower rates.
7.3 Port Selection
Choosing alternative ports can sometimes lead to cost savings, though transit times may be affected.
7.4 Cargo Consolidation
Consolidating shipments to fill containers can improve overall cost-efficiency.
7.5 Digital Platforms and Freight Forwarders
Utilizing digital booking platforms or working with experienced freight forwarders can help in finding competitive rates.
8. Future Outlook for China-US Shipping Rates
Several factors are likely to influence future shipping rates on this route:
8.1 Technological Advancements
Increased adoption of AI, blockchain, and IoT in shipping may lead to improved efficiency and potentially impact rates.
8.2 Environmental Regulations
Stricter emissions standards and the shift towards cleaner fuels may increase operational costs for carriers.
8.3 Trade Policies
Ongoing developments in US-China trade relations will continue to impact shipping volumes and rates.
8.4 Infrastructure Developments
Investments in port infrastructure and expansion projects may alleviate congestion and influence rates.
8.5 Market Consolidation
Further consolidation among shipping lines could affect competition and pricing strategies.
9. Case Study: Impact of Trade Tensions on Shipping Rates
The ongoing trade tensions between China and the US have had a significant impact on shipping rates:
Initial uncertainty led to a surge in shipments as importers rushed to beat tariff deadlines
Subsequent declines in trade volumes put downward pressure on rates
Shifts in manufacturing from China to other Asian countries altered some shipping patterns
Increased focus on Trans-Pacific trade agreements influenced regional shipping dynamics
10. The Role of Alliances in Rate Setting
Major shipping alliances play a crucial role in capacity management and rate stability:
2M Alliance: Maersk and MSC
Ocean Alliance: CMA CGM, COSCO, Evergreen, OOCL
THE Alliance: Hapag-Lloyd, ONE, Yang Ming, HMM
These alliances coordinate capacity and can influence market rates through their collective actions.
11. Environmental Considerations and Green Shipping
Environmental factors are increasingly impacting shipping rates:
IMO 2020 sulphur cap has increased fuel costs
Growing demand for eco-friendly shipping options
Potential carbon taxes or emissions trading schemes
Investments in cleaner technologies may impact future rates
12. Digitalization and Rate Transparency
The shipping industry is undergoing digital transformation, affecting how rates are determined and communicated:
Online booking platforms providing real-time rate information
Increased use of data analytics in pricing strategies
Blockchain technology enhancing transparency in supply chains
Digital freight forwarders offering new pricing models
13. Conclusion
Container shipping rates from China to the US are a complex and dynamic aspect of international trade. They are influenced by a multitude of factors, ranging from global economic conditions to local port efficiencies. As the shipping industry continues to evolve, staying informed about these rates and the factors that influence them is crucial for businesses engaged in trans-Pacific trade.
While recent years have seen unprecedented volatility, the market is showing signs of stabilization. However, challenges such as geopolitical tensions, environmental regulations, and technological disruptions continue to shape the landscape of container shipping.
For shippers and importers, a strategic approach to managing shipping costs, leveraging technology, and staying adaptable to market changes will be key to navigating the complexities of China-US container shipping rates. As global trade patterns continue to evolve, so too will the dynamics of this crucial shipping route, making ongoing analysis and adaptation essential for success in international commerce.
 Easy Shipping From Global, Save Cost
Easy Shipping From Global, Save Cost