Executive Summary
In the ever-evolving landscape of global trade, understanding the nuances of shipping costs between China and the United States is crucial for businesses of all sizes. This comprehensive report delves into the average shipping costs, exploring historical trends, current benchmarks, and future projections. By leveraging data analytics and expert insights, we aim to provide a clear picture of the financial aspects of transpacific shipping.
1. Introduction: The Importance of China-US Shipping
The China-US shipping route is one of the busiest in the world, serving as a vital artery for global commerce. In 2023, the total trade value between these two economic giants exceeded $690 billion, highlighting the critical nature of efficient and cost-effective shipping solutions.
2. Historical Perspective: Shipping Cost Trends (2015-2024)
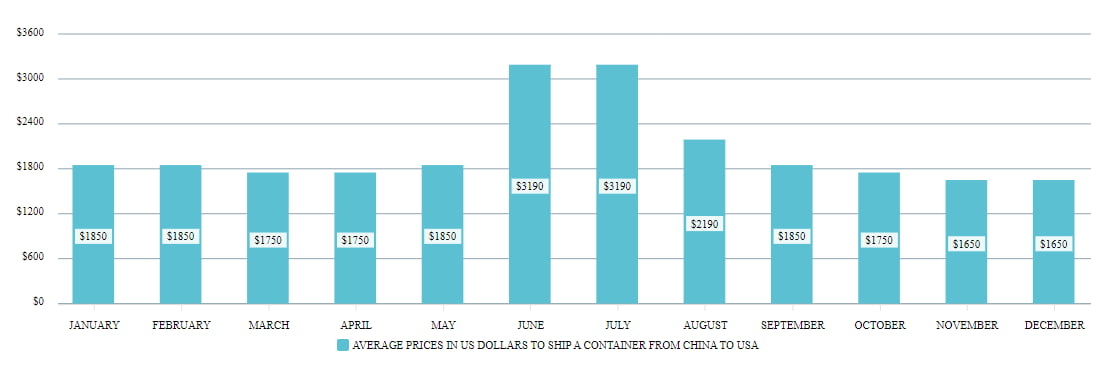
To understand the current landscape, it's essential to examine historical trends. The following chart illustrates the average shipping costs from China to the US over the past decade:
| Year | Average Cost (USD per TEU) | Year-on-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 1,506 | - |
| 2016 | 1,285 | -14.7% |
| 2017 | 1,480 | +15.2% |
| 2018 | 1,834 | +23.9% |
| 2019 | 1,675 | -8.7% |
| 2020 | 3,892 | +132.4% |
| 2021 | 10,839 | +178.5% |
| 2022 | 7,590 | -30.0% |
| 2023 | 2,735 | -64.0% |
| 2024 (Q1-Q2) | 2,150 | -21.4% |
Note: TEU stands for Twenty-Foot Equivalent Unit, a standard measure in shipping.
3. Current Landscape: Average Shipping Costs in 2024
As of 2024, the average shipping cost from China to the US has stabilized compared to the volatility seen in recent years. However, it's crucial to break down these costs by various factors:
3.1 Cost Breakdown by Container Size
| Container Size | Average Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| 20-foot | 2,150 |
| 40-foot | 3,200 |
| 40-foot High Cube | 3,350 |
3.2 Cost Variation by US Destination Port
| Destination Port | Average Cost (USD per TEU) |
|---|---|
| Los Angeles/Long Beach | 1,950 |
| New York/New Jersey | 2,300 |
| Seattle/Tacoma | 2,050 |
| Houston | 2,250 |
| Miami | 2,400 |
4. Factors Influencing Average Shipping Costs
Several key factors contribute to the fluctuation of shipping costs:
Fuel Prices: A 1% increase in fuel prices can lead to a 0.3-0.5% increase in shipping costs.
Trade Imbalances: The ratio of imports to exports affects container availability and pricing.
Seasonal Demand: Costs can increase by 20-30% during peak seasons (e.g., pre-holiday periods).
Regulatory Changes: New environmental regulations can impact costs by 5-10%.
Global Economic Conditions: Economic growth or recession can significantly influence shipping demand and prices.
5. Cost Optimization Strategies
Businesses can employ several strategies to optimize their shipping costs:
Long-term Contracts: Can potentially reduce costs by 10-15%.
Consolidation: Sharing container space can save up to 30% for smaller shipments.
Off-Peak Shipping: Scheduling shipments during less busy periods can save 15-20%.
Digital Platforms: Using online booking platforms can reduce costs by 5-8% through increased transparency and competition.
Alternative Ports: Considering less congested ports can lead to savings of 10-15% in some cases.
6. Future Projections: 2025-2030
Based on current trends and expert analyses, we project the following scenarios for China-US shipping costs:
| Scenario | Projected Average Cost (USD per TEU) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Base Case | 2,300 - 2,800 | Stable economic growth, gradual technological improvements |
| High-Cost Scenario | 3,500 - 4,000 | Increased fuel costs, stricter environmental regulations |
| Low-Cost Scenario | 1,800 - 2,200 | Technological breakthroughs, increased competition |
7. Emerging Trends and Their Impact on Shipping Costs
Several emerging trends are likely to shape the future of China-US shipping costs:
Green Shipping Initiatives: Potential to increase costs by 5-10% in the short term but lead to long-term efficiencies.
Blockchain Technology: Could reduce administrative costs by 15-20% through improved transparency and efficiency.
Autonomous Vessels: May reduce operational costs by 10-15% once fully implemented.
3D Printing: Could potentially reduce the volume of shipped goods by 5-10% for certain industries.
Trade Policy Changes: Ongoing negotiations and potential new agreements could impact tariffs and overall shipping demand.
8. Case Study: Impact of COVID-19 on Shipping Costs
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on shipping costs, as illustrated by the following data:
| Period | Average Cost (USD per TEU) | % Change from Pre-Pandemic |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Pandemic (2019) | 1,675 | - |
| Peak Pandemic (2021) | 10,839 | +547% |
| Post-Peak (2023) | 2,735 | +63% |
| Current (2024) | 2,150 | +28% |
This case study demonstrates the extreme volatility that external factors can introduce into shipping costs and the importance of resilient supply chain strategies.
9. Comparative Analysis: China-US vs. Other Major Shipping Routes
To provide context, here's how the China-US route compares to other major global shipping routes:
| Route | Average Cost (USD per TEU) | % Difference from China-US |
|---|---|---|
| China - US | 2,150 | - |
| China - Europe | 1,950 | -9.3% |
| Europe - US | 1,800 | -16.3% |
| China - Australia | 1,650 | -23.3% |
| US - South America | 1,750 | -18.6% |
10. Conclusion and Recommendations

The average shipping cost from China to the US remains a critical factor in global trade dynamics. While costs have stabilized from the pandemic-induced spikes, they remain higher than pre-pandemic levels. Businesses engaged in China-US trade should consider the following recommendations:
Diversify Suppliers: Reduce reliance on single sources to mitigate risk.
Invest in Predictive Analytics: Utilize data to forecast cost fluctuations and optimize shipping schedules.
Explore Alternative Transportation Methods: Consider air freight or rail options for time-sensitive or high-value goods.
Negotiate Flexible Contracts: Incorporate clauses that allow for adjustments based on market conditions.
Stay Informed: Regularly monitor global economic indicators, trade policies, and technological advancements that may impact shipping costs.
By staying informed and adaptable, businesses can navigate the complexities of China-US shipping costs and maintain competitive advantage in the global marketplace.
 Easy Shipping From Global, Save Cost
Easy Shipping From Global, Save Cost